Pfizer vaccine appears to be effective against UK coronavirus variant
A study showed that a lab-made coronavirus carrying all the mutations of the B.1.1.7 variant was neutralised by antibodies.

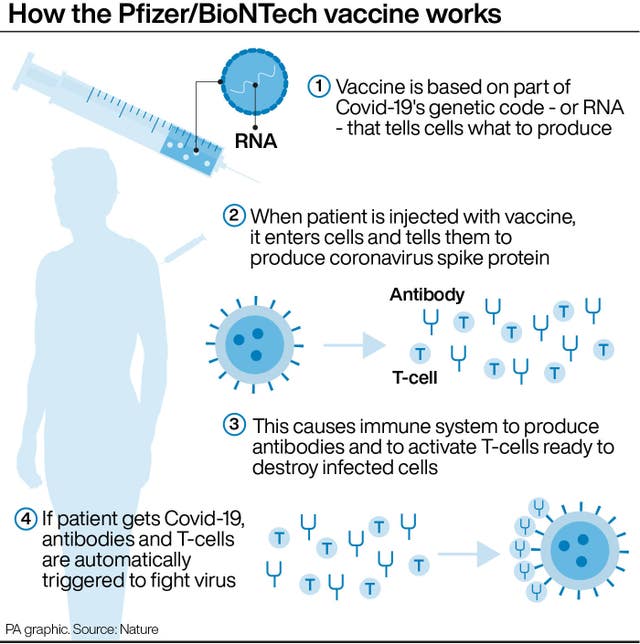
A Covid-19 vaccine developed by Pfizer and BioNTech appears to protect against a coronavirus variant spreading rapidly across the UK.
The results come amid growing fears that the variant, dubbed B.1.1.7, has mutations that may reduce the effectiveness of the vaccines designed to protect against Covid-19.
In a new study, which has not yet been peer-reviewed, researchers from BioNTech collected blood samples from 16 people who had received the Pfizer vaccine in previous clinical trials.
They found that a lab-made version of the virus – with all the mutations resembling the B.1.1.7 variant – was neutralised by antibodies.
The researchers said their results indicate its is “unlikely that the B.1.1.7 lineage will escape BNT162b2-mediated (Pfizer/BionTech vaccine) protection”.
A similar study from the pharmaceutical giant earlier this month showed the vaccine to be effective against a key mutation called N501Y.
The mutation is present in the UK variant, as well as another highly transmissible new variant that has emerged in South Africa.
Pfizer said it had tested 16 different mutations in the variants and none had any significant impact on how the vaccine worked.
Dr Simon Clarke, an associate professor in cellular microbiology at the University of Reading, described the recent research as “positive”, saying: “The so-called ‘Kent variant’ of the Covid-19 coronavirus is no less susceptible to neutralisation by antibodies produced in response to Pfizer-BioNTech’s vaccine.
“This experimental evidence confirms earlier predictions.
“We await similar studies on other variants, particularly from South Africa and Brazil.”
He warned the research does not take into account the effect mutations may have on T-cell immunity – which are also key players in the immune response to viral infection.
Dr Clarke said: “While this study confirms that the antibody response is not blunted by the mutations in this variant, it does not assess the effect that these may have on T-cell immunity, so it remains entirely possible that they could indeed have an adverse effect on vaccine-induced immunity.”
Danny Altmann, professor of immunology at Imperial College London and British Society for Immunology spokesperson, said the findings showed “a slight reduction” in neutralisation against the UK variant but he hoped the reduction was “not enough to impair protection”.
However, he also warned that more evidence is emerging on other coronavirus variants where scientists are “finding some quite disturbing effects on neutralisation”.





